Get Started - Busbar Trunking System (BTS)
A Busbar Trunking System (BTS) is a modern and efficient method of distributing electrical power throughout a building or facility. Instead of traditional cables, it uses prefabricated sections of busbars (copper or aluminum conductors) enclosed within protective housing.
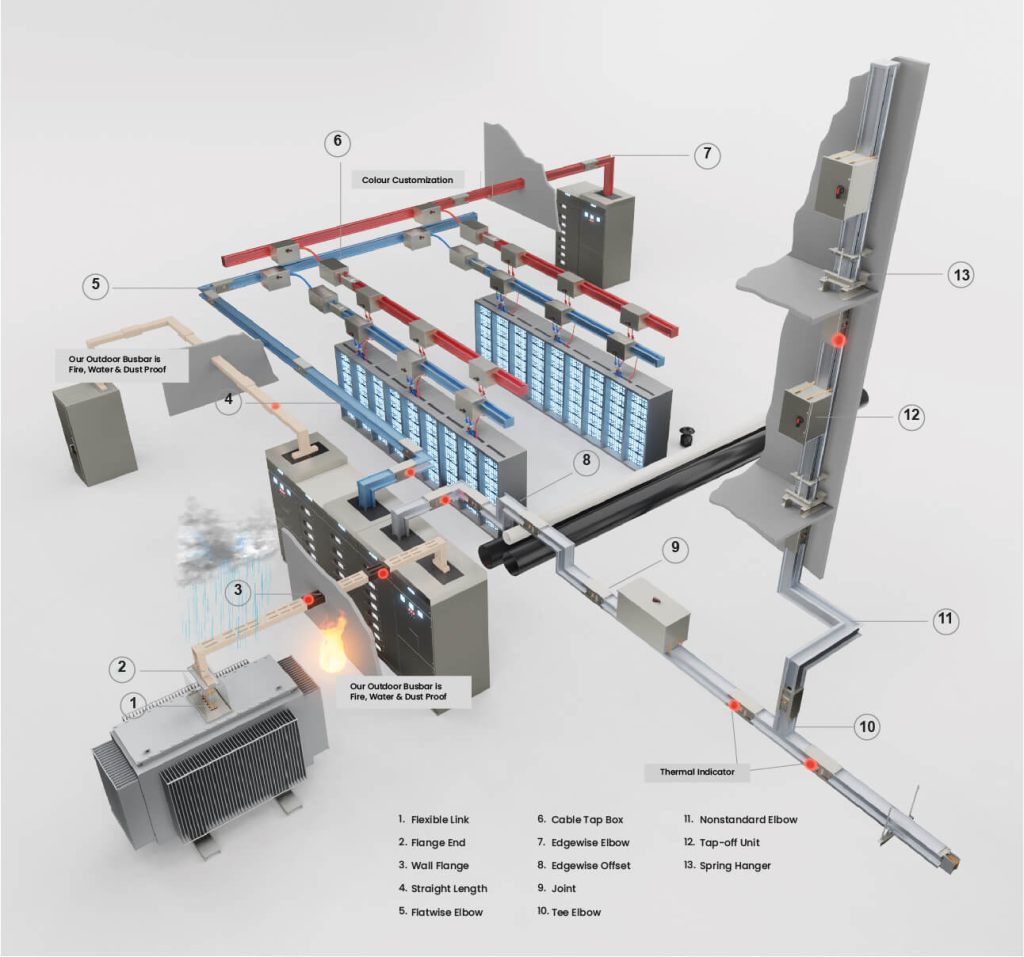
Advantages of Busbar Trunking Systems
- Flexibility: Easily customizable with tap-off boxes placed along the busbar run, allowing power connections at various points without major wiring changes. This facilitates future system modifications and expansions.
- Space Efficient: BTS takes up less space compared to traditional cable installations, especially in high-power applications.
- Faster Installation: Prefabricated sections and easy-to-use connection joints significantly reduce installation time and labor compared to complex cable runs.
- Reliability: Durable construction and enclosed design provides superior protection and reduced maintenance needs.
- Scalability: It’s simple to extend or reconfigure a BTS as power requirements change.
- Reduced Fire Risk: Some BTS may offer a degree of fire resistance.
Key Components & Applications
- Busbars: Insulated copper or aluminum conductors that carry the electrical current.
- Housing: Usually metal enclosure (sheet steel or aluminum) providing protection and structural support.
- Joints: Connection points between busbar sections, ensuring proper electrical and mechanical continuity.
- Tap-Off Boxes: Allow power to be tapped from the busbar at any point.
- Accessories: End-feed units, elbows, expansion joints, flanges, etc., to accommodate the building layout.
Types of Busbar Trunking Systems
- Sandwich-Type: Most common in low to medium power applications. Conductors are tightly sandwiched between insulation.
- Air-Insulated: Popular in higher power applications as they offer better heat dissipation. Conductors are spaced apart with air as the primary insulation.
Applications
- Commercial Buildings: Shopping centers, airports, and hospitals due to their space-saving and flexibility advantages.
- Industrial Facilities: Manufacturing plants and factories where power distribution needs might change frequently.
- Data Centers: Provides reliable and adaptable power distribution for critical IT infrastructure.
- High-Rise Buildings: Offers a convenient way to distribute power throughout multiple floors.
